
1.HbA1c Level as a Predictor of Future Type 2 Diabetes Risk |
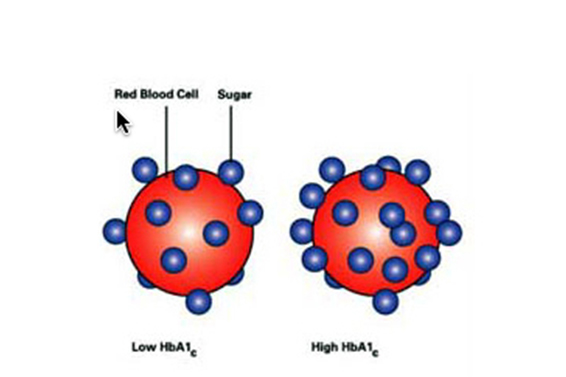
![]() A new study conducted by Leong et.al, published in the journal ‘Diabetes Care’, has revealed the usefulness of HbA1c levels as a predictive factor for type 2 diabetes risk. According to the study which involved middle aged whites (n=11,244) and blacks (n=2,294) without diabetes from the Framingham Heart Study and Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study, 3,315 individuals developed diabetes over 20 years.
A new study conducted by Leong et.al, published in the journal ‘Diabetes Care’, has revealed the usefulness of HbA1c levels as a predictive factor for type 2 diabetes risk. According to the study which involved middle aged whites (n=11,244) and blacks (n=2,294) without diabetes from the Framingham Heart Study and Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study, 3,315 individuals developed diabetes over 20 years.
![]() When the link between HbA1c levels and diabetes was assessed, a fourfold increased risk of developing T2DM was noted for each percentage-unit increase in HbA1c (odds ratio 4 for Blacks and 4.73 for Whites resulting in a combined OR of 4.50). After adjustment for fasting laboratory tests and clinic data, the combined odds ratios were 2.68 over 20 years, 5.79 within 8 years, and 2.23 after 8 years.
When the link between HbA1c levels and diabetes was assessed, a fourfold increased risk of developing T2DM was noted for each percentage-unit increase in HbA1c (odds ratio 4 for Blacks and 4.73 for Whites resulting in a combined OR of 4.50). After adjustment for fasting laboratory tests and clinic data, the combined odds ratios were 2.68 over 20 years, 5.79 within 8 years, and 2.23 after 8 years.
![]() The study thus points out that HbA1c levels may be used to predict T2DM in different common scenarios and is useful for identifying individuals with elevated T2DM risk in both the short- and long-term.
The study thus points out that HbA1c levels may be used to predict T2DM in different common scenarios and is useful for identifying individuals with elevated T2DM risk in both the short- and long-term.
![]()
For enquiries info@jothydev.net.
Please visit: jothydev.net | research.jothydev.com | diabscreenkerala.net | jothydev.com/newsletter
