
7. Drug and device update
G4 Insulin Pump from Tandem Diabetes Care wins FDA approval
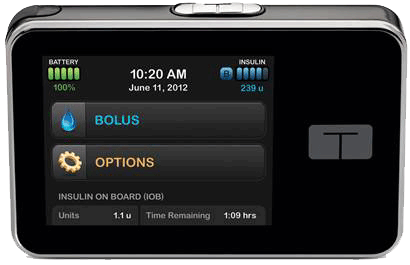
![]() FDA has approved its t:slim G4 touch screen insulin pump with continuous glucose monitoring integration. The pump, designed for people 12 years and older, combines features of Tandem’s pump technology with Dexcom’s CGM technology.
FDA has approved its t:slim G4 touch screen insulin pump with continuous glucose monitoring integration. The pump, designed for people 12 years and older, combines features of Tandem’s pump technology with Dexcom’s CGM technology.
 |
Glucagon nasal powder for hypoglycemia
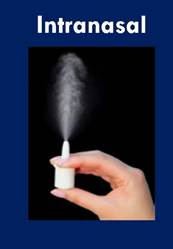
![]() Glucagon in the form of nasal powder was effective in managing hypoglycemia in children and teens with type 1 diabetes. The glucagon nasal powder (GNP) comes in a single-use device that injects into a patient's nose, entering the body through the mucus.
Glucagon in the form of nasal powder was effective in managing hypoglycemia in children and teens with type 1 diabetes. The glucagon nasal powder (GNP) comes in a single-use device that injects into a patient's nose, entering the body through the mucus.
![]() In a study, 16 caregivers were paired with a diabetes patient, who taught the caregivers how to use either a needle with glucagon and powder or glucagon nasal powder. One week later, caregivers were asked to treat a manikin. Fifteen of the 16 caregivers successfully administered a full dose with the nasal device, compared to only eight of 16 with injection rescues. A separate group tested 15 volunteers, who were not associated with anybody who had diabetes and were not trained, but were shown the devices prior to the simulation. Only three of the participants in the volunteer group injected any glucagon with the needle, and none gave a full dose. In comparison, 14 of 15 volunteers injected a full dose with the glucagon nasal powder device.
In a study, 16 caregivers were paired with a diabetes patient, who taught the caregivers how to use either a needle with glucagon and powder or glucagon nasal powder. One week later, caregivers were asked to treat a manikin. Fifteen of the 16 caregivers successfully administered a full dose with the nasal device, compared to only eight of 16 with injection rescues. A separate group tested 15 volunteers, who were not associated with anybody who had diabetes and were not trained, but were shown the devices prior to the simulation. Only three of the participants in the volunteer group injected any glucagon with the needle, and none gave a full dose. In comparison, 14 of 15 volunteers injected a full dose with the glucagon nasal powder device.
![]() The nasal powder seems easier to administer and there were no clinical outcomes. This device might evolve as a better, easier and less expensive option to treat hypoglycemia.
The nasal powder seems easier to administer and there were no clinical outcomes. This device might evolve as a better, easier and less expensive option to treat hypoglycemia.
Omarigliptin safe for Type 2 diabetes patients
![]() A once-weekly dose of omarigliptin for 12 weeks reduced HbA1c, 2-hour postprandial glucose and fasting plasma glucose in adults with type 2 diabetes. In an additional extension study to evaluate the longer-term safety and tolerability of 25 mg omarigliptin for 66 weeks, researchers found that, when compared with placebo/metformin therapy, adverse events remained similar between treatment groups, hypoglycemia was rare and the drug was well tolerated.
A once-weekly dose of omarigliptin for 12 weeks reduced HbA1c, 2-hour postprandial glucose and fasting plasma glucose in adults with type 2 diabetes. In an additional extension study to evaluate the longer-term safety and tolerability of 25 mg omarigliptin for 66 weeks, researchers found that, when compared with placebo/metformin therapy, adverse events remained similar between treatment groups, hypoglycemia was rare and the drug was well tolerated.
![]() Researchers analyzed data from 685 adults from 21 countries with type 2 diabetes randomly assigned to one of five once-weekly doses of omarigliptin (0.25 mg, 1 mg, 3 mg, 10 mg or 25 mg) or placebo for 12 weeks. Within the cohort, 485 participants entered the 66-week extension study that immediately followed.
Researchers analyzed data from 685 adults from 21 countries with type 2 diabetes randomly assigned to one of five once-weekly doses of omarigliptin (0.25 mg, 1 mg, 3 mg, 10 mg or 25 mg) or placebo for 12 weeks. Within the cohort, 485 participants entered the 66-week extension study that immediately followed.
![]() After 12 weeks of treatment, researchers found that all doses of omarigliptin reduced HbA1c and postprandial glucose when compared with placebo, and that all doses greater than 1 mg reduced FPG when compared with placebo. The 25-mg omarigliptin dose provided the greatest reduction in HbA1c (least-squares mean change from baseline vs. placebo, –0.72%), postprandial glucose (–45 mg/dl) and FPG (–23.4 mg/dl).
After 12 weeks of treatment, researchers found that all doses of omarigliptin reduced HbA1c and postprandial glucose when compared with placebo, and that all doses greater than 1 mg reduced FPG when compared with placebo. The 25-mg omarigliptin dose provided the greatest reduction in HbA1c (least-squares mean change from baseline vs. placebo, –0.72%), postprandial glucose (–45 mg/dl) and FPG (–23.4 mg/dl).
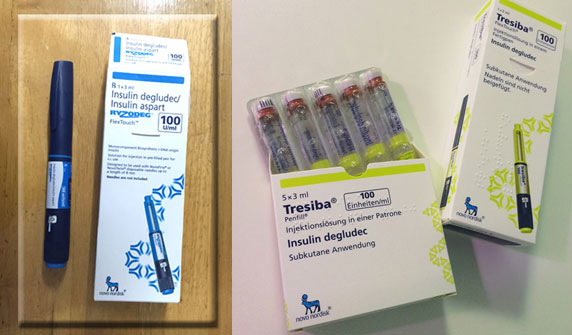
FDA approves Ryzodeg and Tresiba
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Ryzodeg and Tresiba for use in type 2 diabetes based on the interim results of the cardiovascular trial for insulin degludec called DEVOTE. Ryzodeg 70/30 contains insulin aspart, a rapid-acting agent, as well as insulin degludec.
![]() Tresiba contains only insulin degludec as the active ingredient. Because of the drug's extended coverage, patients do not need to take it the same time each day as with other basal insulins, leading some to call it the "Sunday-sleeping-in insulin". These medications are available, widely popular and approved in many parts of the world including India since several years.
Tresiba contains only insulin degludec as the active ingredient. Because of the drug's extended coverage, patients do not need to take it the same time each day as with other basal insulins, leading some to call it the "Sunday-sleeping-in insulin". These medications are available, widely popular and approved in many parts of the world including India since several years.
 |
For enquiries info@jothydev.net.
Please visit: jothydev.net | research.jothydev.com | diabscreenkerala.net | jothydev.com/newsletter
