
7. Device and Drug Updates
Dapagliflozin combination found effective in type 2 diabetes
![]()
 Dapagliflozin as an add-on to metformin and sulfonylurea improved glycemic control and reduced body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to recent study findings published in Diabetes Care.
Compared with the placebo group, the dapagliflozin group had significantly reduced HbA1c levels from baseline to 24 weeks (P<.0001). At week 24, more patients on dapagliflozin achieved a therapeutic glycemic response compared with those receiving placebo (P<.0001). Fasting plasma glucose and body weight also decreased more throughout the study period among the dapagliflozin group compared with placebo (both P<.0001).
From baseline to week 8, patients assigned dapagliflozin had a significantly greater reduction in seated systolic blood pressure compared with those assigned placebo (P=.025).
The placebo (51.4%) and dapagliflozin (48.6%) groups had similar rates of adverse events. Compared with the placebo group, the dapagliflozin group experienced more events of hypoglycemia (P=.024) and genital infections (P=.029).
Dapagliflozin as an add-on to metformin and sulfonylurea improved glycemic control and reduced body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to recent study findings published in Diabetes Care.
Compared with the placebo group, the dapagliflozin group had significantly reduced HbA1c levels from baseline to 24 weeks (P<.0001). At week 24, more patients on dapagliflozin achieved a therapeutic glycemic response compared with those receiving placebo (P<.0001). Fasting plasma glucose and body weight also decreased more throughout the study period among the dapagliflozin group compared with placebo (both P<.0001).
From baseline to week 8, patients assigned dapagliflozin had a significantly greater reduction in seated systolic blood pressure compared with those assigned placebo (P=.025).
The placebo (51.4%) and dapagliflozin (48.6%) groups had similar rates of adverse events. Compared with the placebo group, the dapagliflozin group experienced more events of hypoglycemia (P=.024) and genital infections (P=.029).
Read More
Bladder Cancer Risk with Pioglitazone Disproved?
![]() In a multipopulation pooled, cumulative exposure analysis published in Diabetologia, the cumulative use of pioglitazone or rosiglitazone was not associated with the incidence of bladder cancer.
Data were collated on 1.01 million persons over 5.9 million person-years. There were 3,248 cases of incident bladder cancer, with 117 exposed cases and a median follow-up duration of 4.0 to 7.4 years. Overall, there was no evidence for any association between cumulative exposure to pioglitazone and bladder cancer in men or women after adjustment for age, calendar year, diabetes duration, smoking and any ever use of pioglitazone. No association was observed between rosiglitazone and bladder cancer in men or women.
In a multipopulation pooled, cumulative exposure analysis published in Diabetologia, the cumulative use of pioglitazone or rosiglitazone was not associated with the incidence of bladder cancer.
Data were collated on 1.01 million persons over 5.9 million person-years. There were 3,248 cases of incident bladder cancer, with 117 exposed cases and a median follow-up duration of 4.0 to 7.4 years. Overall, there was no evidence for any association between cumulative exposure to pioglitazone and bladder cancer in men or women after adjustment for age, calendar year, diabetes duration, smoking and any ever use of pioglitazone. No association was observed between rosiglitazone and bladder cancer in men or women.
Read More
Self Administering Smart Insulin is the future in type 1 diabetes
![]() Researchers from the University of Utah has created Ins-PBA-F, a long lasting 'smart insulin' that self activates when blood glucose levels rise. Results from the diabetic mouse models show that one injection works for a minimum of 14 hours. Throughout this period, the synthetic insulin appeared to repeatedly and automatically lower blood glucose after mice were given large amounts of sugar. Ins-PBA-F may be quicker and more effective in lowering blood glucose than long-acting insulin detemir, according to the researchers, who also notes that the speed and kinetics of bringing blood glucose down to safe levels were identical in diabetic mouse models treated with Ins-PBA-F and healthy mice whose blood glucose is regulated by their own insulin.
Researchers from the University of Utah has created Ins-PBA-F, a long lasting 'smart insulin' that self activates when blood glucose levels rise. Results from the diabetic mouse models show that one injection works for a minimum of 14 hours. Throughout this period, the synthetic insulin appeared to repeatedly and automatically lower blood glucose after mice were given large amounts of sugar. Ins-PBA-F may be quicker and more effective in lowering blood glucose than long-acting insulin detemir, according to the researchers, who also notes that the speed and kinetics of bringing blood glucose down to safe levels were identical in diabetic mouse models treated with Ins-PBA-F and healthy mice whose blood glucose is regulated by their own insulin.
Read More
Inhaled Insulin launched in US
![]()
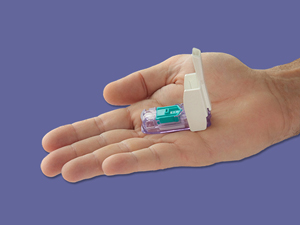 Sanofi launched an inhalable insulin, Afrezza(Developed by Mannkind), the only inhalable insulin in US. Inhalation promises to be faster acting and much more convenient than injections. Afrezza, which uses a whistle-sized inhaler and works to control blood-sugar levels in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, was approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration in June.
Afrezza should not be used in patients with asthma, or those suffering from certain complications, however. It is also not recommended for smokers or recent ex-smokers.
Sanofi launched an inhalable insulin, Afrezza(Developed by Mannkind), the only inhalable insulin in US. Inhalation promises to be faster acting and much more convenient than injections. Afrezza, which uses a whistle-sized inhaler and works to control blood-sugar levels in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, was approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration in June.
Afrezza should not be used in patients with asthma, or those suffering from certain complications, however. It is also not recommended for smokers or recent ex-smokers.
For enquiries info@jothydev.net.
Please visit: jothydev.net | research.jothydev.com | diabscreenkerala.net | jothydev.com/newsletter
